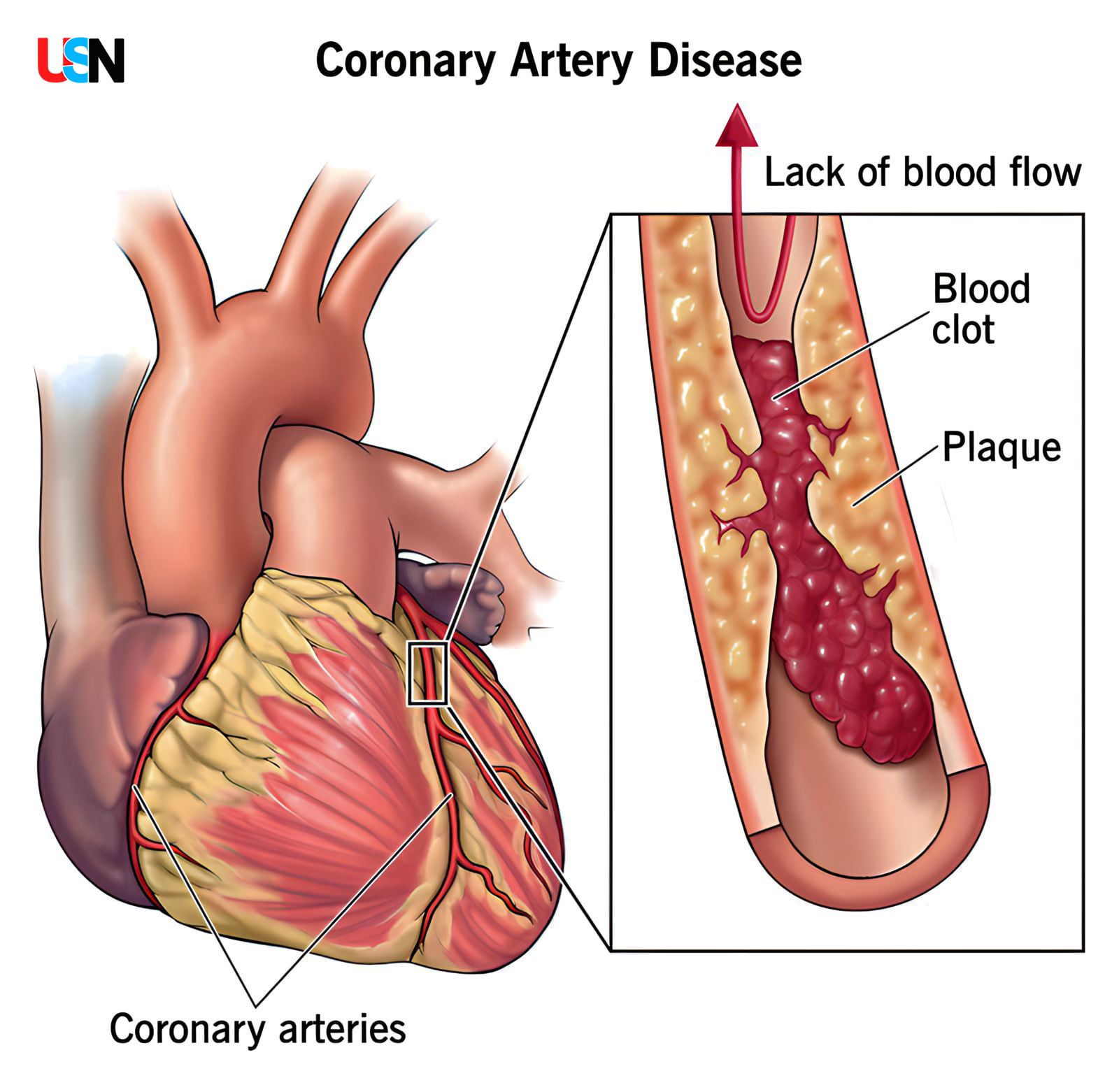
Coronary Artery Disease (CAD), also known as coronary heart disease or atherosclerotic heart disease, is a common and potentially serious cardiovascular condition. It occurs when the coronary arteries, which supply oxygen-rich blood to the heart muscle, become narrowed or blocked due to a buildup of fatty deposits called plaques on the inner walls of the arteries. These plaques consist of cholesterol, calcium, and other substances.
Here’s a detailed overview of Coronary Artery Disease:
- Causes and Risk Factors:
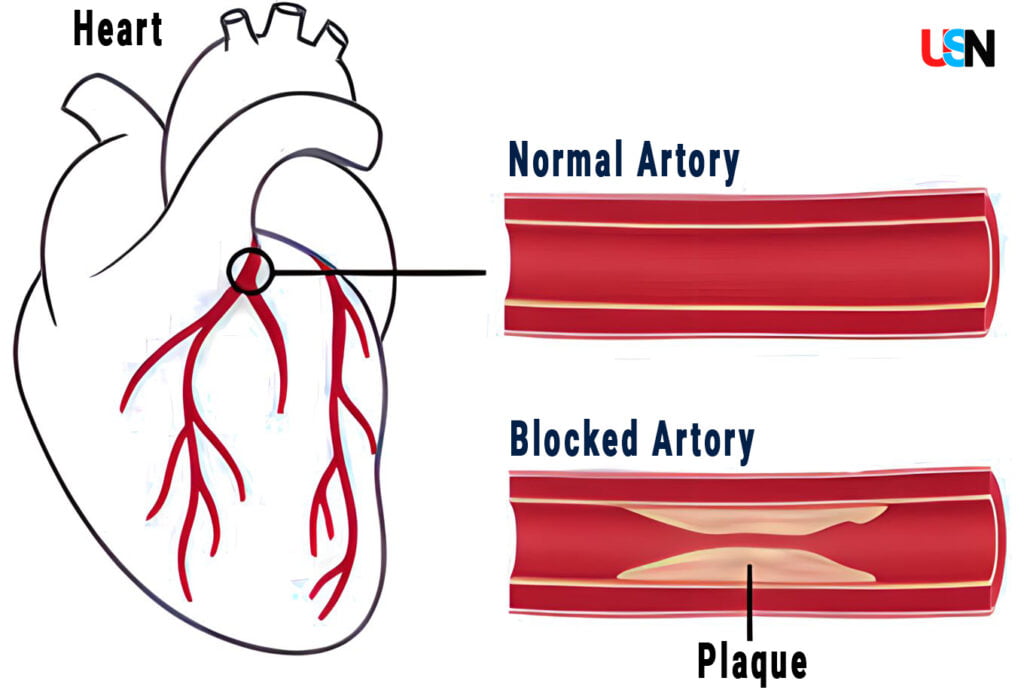
- The primary cause of CAD is atherosclerosis, a condition where plaques gradually form and narrow the coronary arteries, reducing blood flow to the heart.
- Several risk factors can contribute to the development of CAD, including:
- Smoking: Tobacco use is a significant risk factor for CAD, as it damages blood vessels and accelerates atherosclerosis.
- High Blood Pressure: Hypertension strains the arterial walls, increasing the risk of plaque formation.
- High Cholesterol Levels: Elevated LDL (low-density lipoprotein) cholesterol, often referred to as “bad cholesterol,” can lead to plaque buildup.
- Diabetes: Individuals with diabetes have a higher risk of CAD due to underlying metabolic abnormalities.
- Obesity and Inactivity: Being overweight and leading a sedentary lifestyle are associated with an increased risk of CAD.
- Family History: A family history of early heart disease can raise the likelihood of developing CAD.
- Age and Gender: The risk of CAD increases with age, and men generally have a higher risk compared to pre-menopausal women (although this difference narrows after menopause).
2. Symptoms:
- CAD can have a range of symptoms, which can vary from mild to severe. Some common symptoms include:
- Chest pain or discomfort (angina): This is often described as a squeezing, pressure-like, or burning sensation in the chest, usually triggered by physical or emotional stress.
- Shortness of breath: Especially during exertion or physical activity.
- Fatigue: Feeling tired and weak, especially with increased activity.
- Heart attack (Myocardial Infarction): If a plaque ruptures and completely blocks a coronary artery, it can lead to a heart attack, which may cause severe chest pain, radiating pain in the arms or jaw, nausea, sweating, and shortness of breath.
3. Diagnosis:
- CAD is typically diagnosed through a combination of medical history evaluation, physical examination, and diagnostic tests.
- Common diagnostic tests include Electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG), Stress Test, Echocardiography, Coronary Angiography, and Cardiac CT Scan or MRI.
4. Treatment:
- The management of CAD aims to reduce symptoms, prevent complications, and lower the risk of heart attacks and other cardiovascular events.
- Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role and may include adopting a heart-healthy diet, engaging in regular physical activity, quitting smoking, and managing stress.
- Medications: Various drugs can be prescribed, such as statins to lower cholesterol, antiplatelet agents to prevent blood clots, beta-blockers to control blood pressure and heart rate, and nitroglycerin for angina relief.
- In more severe cases or when lifestyle and medication are insufficient, medical procedures like angioplasty with stent placement or coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) may be considered to improve blood flow to the heart.
5. Prevention:
- Preventive measures are crucial to reduce the risk of developing CAD or slowing its progression.
- Lifestyle changes, such as maintaining a healthy diet, regular exercise, not smoking, and managing underlying conditions like diabetes and hypertension, are essential for prevention.
- Regular check-ups with a healthcare provider are crucial, especially if there’s a family history of heart disease or if someone has multiple risk factors.
Coronary Artery Disease is a serious health condition, but with appropriate management and lifestyle changes, its impact can be significantly reduced, and the risk of complications can be minimized. Anyone experiencing symptoms related to CAD should seek medical attention promptly to receive appropriate evaluation and treatment.